
So, to run a CPU stability test you have to: The purpose of a processor stability test is to determine how smoothly the CPU works, even if it is under high load. Thus, FPS is a good indicator while running a CPU stability test. However, if the frame rate drops below 30 FPS, it means that something is wrong (for example, the system cannot keep up with the current workload). As a rule, in most cases, browsers render frames at a speed of 60 FPS (although sometimes a slightly lower speed may be acceptable). The number of frames per second (abbreviated as FPS) indicates how fast your browser is able to render new frames. As you might have guessed, the number of points directly depends on the speed and the test duration. The number of score points indicates how many hashes were computed during the test. Thus, more power and threads will provide higher speed and CPU load (for example, 50% power + 10 threads will result in a 500% load). Since the power and the number of threads almost proportionally affect the speed, a 100% power + 1 thread will give the same speed as 50% power + 2 threads, or 25% power + 4 threads.
Overdrive cpu stress test full#
The power indicates how much CPU time can be used by one thread (for example, 100% power means full speed without time idle). Multi-core CPUs cope better with the multithreading, this is why in such cases modern processors work faster and get better results. Thus, more threads lead to a higher speed, but at the same time to a higher load. The number of threads determines the number of simultaneous operations for computing hashes. However, you need to remember that for maximum speed you need to use the full power of the CPU (that is, specify as many threads and power as possible). Obviously, a more powerful processor develops a higher speed. The speed measures how fast the processor is, and is measured in the number of hash operations per second. Given that not all processors and devices withstand high loads, it is strongly recommended to gradually increase indicator values.
Overdrive cpu stress test how to#
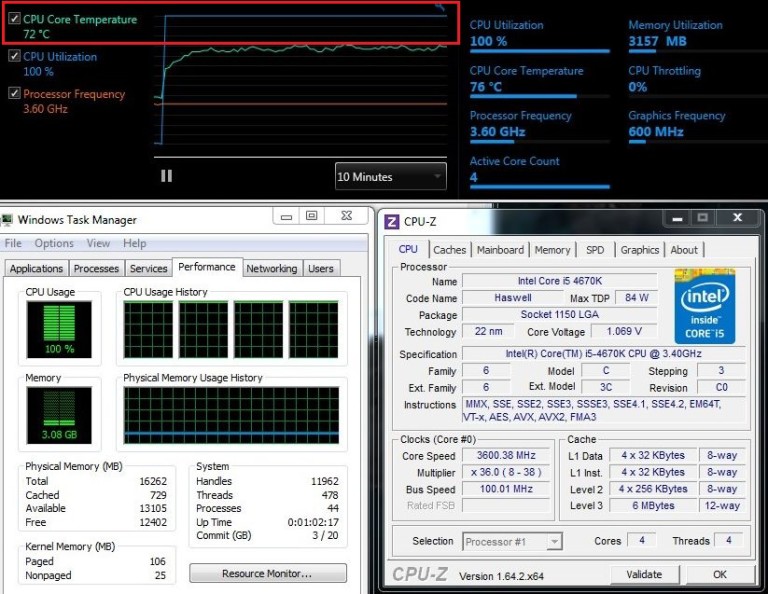
I watched this YouTube video below that does a great job explaining what PBO and Curve Optimizer do, and how to find the optimal settings for your system.Power -5 +5 Start CPU Stress Test What do the indicators mean?īefore starting the CPU stress test, review the indicators below to understand what they are for. I have a Thermaltake 240mm AIO Cooler which does a pretty good job keeping temps stable. With this I got results of 4700 MHz single core and 4350 MHz all-core clockings stable with no increase in temperatures compared to stock settings under full load or otherwise. I ended up using a +150 MHz boost with a Curve Optimization of negative 18 for each individual core. What actually even makes a bigger difference in the results is using the Curve Optimizer along with PBO to get optimized frequencies and voltages/temperatures. I ended up disabling the PBO options in the AI Tweaker section and manually set the PBO options in the Advanced Overclocking section.

The one under AI Tweaker is a milder version that has less performance gains and would not void the warranty compared to the one under the Advanced menu Overclock section which clearly gives a warning that changing the settings in this section will void the warranty. Seems the two different sections serve two different purposes. I just played around with these settings today with my Ryzen 5900X and X570-E Gaming motherboard. Further evidence of this is that they don't sync if you disable PBO in one, it will not disable on the other.Ĭan someone knowledgeable please explain this mess?Įxample images just to show the two different paths (the values for the options are not what I'm using): It is clear that despite being named the same and having very similar sub-options, these two features are completely different. Whereas turning on the PBO under the Advanced tab on with the same sub-options (and Curve Optimizer on Auto), power draw stays at 76W, the normal power draw constraint. Upon further testing I have noticed that both PBOs behave vastly differently: turning the one under AI Tweaker on, my 5600x's power consumption shoots from 76W (stock draw) to 95W or more (it's also worth noting that turning on "AMD Performance Enhancer" under the same AI Tweaker menu has the same effect, and I've found no practical difference between enabling either that or PBO). Both have nearly the same options except that the latter allows you to change the Curve Optimizer function while the former does not (which is silly, and a complaint I've made here). In my BIOS for the B550-E Gaming you can reach "Precision Boost Overdrive" via two different routes: the "AI Tweaker" tab or or the "Advanced" tab.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
